Moz Q&A is closed.
After more than 13 years, and tens of thousands of questions, Moz Q&A closed on 12th December 2024. Whilst we’re not completely removing the content - many posts will still be possible to view - we have locked both new posts and new replies. More details here.
My Website Page Speed is not increasing
-
HEY EXPERTS,
My website page speed is not increasing. I used the wp rocket plugin but still, I am facing errors of Reduce unused CSS, Properly size images, and Avoid serving legacy JavaScript to modern browsers. you can see in the image
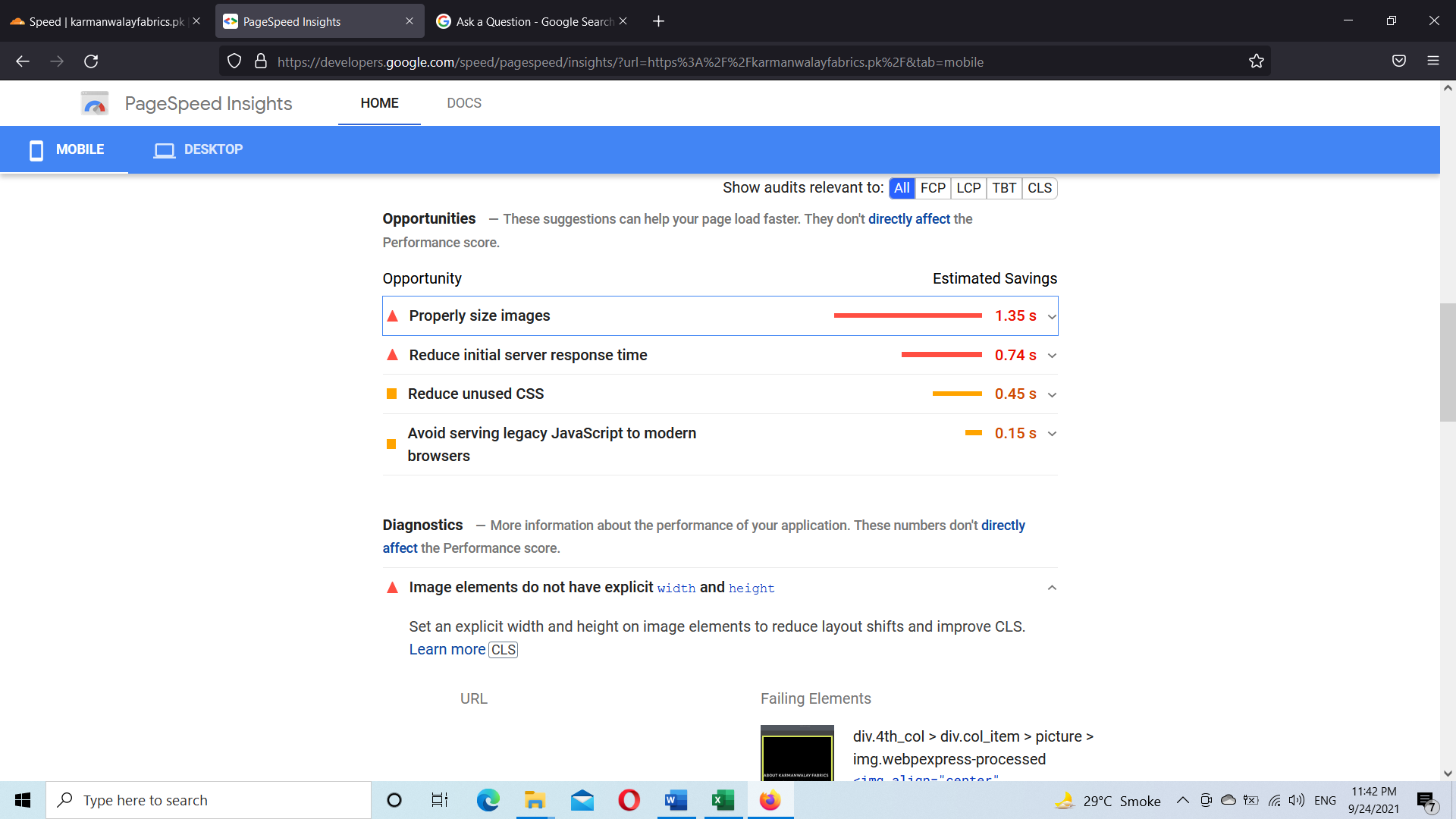
I used many plugins for speed optimization but still facing errors. I optimized the images manually by using photoshop but still, I am facing the issue of images size.
After Google Core Web Vital Update my website keyword position is down due to slow speed. Please guide me on how I increase the page speed of my website https://karmanwalayfabrics.pk
Thanks
-
A variety of factors can contribute to a website's slow page speed, and addressing them requires a systematic approach. Here are some common reasons why your website's page speed might not be increasing:
- Large and Unoptimized Images:
High-resolution images and graphics can significantly slow down page load times. Make sure your images are properly resized, compressed, and served in the appropriate format (JPEG, PNG, WebP).
- Too Many HTTP Requests:
Each element on a web page, such as images, scripts, and stylesheets, requires a separate HTTP request. Limit the number of elements and use techniques like image sprites, CSS and JavaScript minification, and combining files where possible.
- Unoptimized Code:
Bloated or inefficient HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code can increase load times. Optimize your code by removing unnecessary characters, white spaces, and comments, and consider using asynchronous loading for JavaScript.
- Server Performance:
Slow server response times can significantly impact page speed. Choose a reliable web hosting provider with good server performance, and consider using Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to distribute content across multiple servers.
- Lack of Browser Caching:
Enable browser caching to allow returning visitors to load your site faster by storing certain elements locally on their devices.
- Render-Blocking Resources:
JavaScript and CSS files that block the rendering of the page can lead to slower load times. Minimize the use of render-blocking resources and use techniques like asynchronous and deferred loading.
7.Redirects and Broken Links:
Excessive redirects and broken links can increase load times and frustrate users. Minimize redirects and regularly check for broken links.
- External Embedded Media:
Embedded media from external sources (videos, social media widgets, etc.) can slow down your site if not optimized properly. Use lazy loading for media and ensure external sources are not causing delays.
- Database and Plugin Overload:
Excessive database queries and numerous plugins can slow down your website. Optimize your database, use efficient plugins, and eliminate those that are not essential.
- Mobile Responsiveness:
A lack of mobile responsiveness can lead to slow loading times on mobile devices. Ensure your website is fully responsive and optimized for various screen sizes.
- Unoptimized Third-Party Scripts:
Third-party scripts, such as analytics trackers and social media plugins, can impact performance. Evaluate the necessity of these scripts and their impact on load times.
- Too Many Ads:
Excessive ads or poorly optimized ad code can slow down your website. Ensure that ads are properly managed and optimized for performance.
To address these issues, you may need to conduct a thorough website audit, use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or Pingdom to identify specific problems, and then implement the necessary optimizations. Remember that improving page speed is an ongoing process, and regularly monitoring and maintaining your website's performance is crucial for a fast and user-friendly experience.
-
Improving your website's speed, especially in the context of Google's Core Web Vitals, can sometimes require a more detailed approach beyond just using plugins. Here's a guide to address the specific issues you mentioned:
Reduce Unused CSS:
- Manual Cleaning: Sometimes plugins or themes may add unnecessary CSS. You can manually review your CSS files to remove any unused styles.
- Use Tools: There are tools like PurgeCSS that can help to remove unused CSS.
- Minify CSS: If not already done, ensure that your CSS is minified. WP Rocket should handle this, but you can double-check.
Properly Size Images:
- Responsive Images: Make sure you're using the srcset attribute on img tags. WordPress generally does this automatically for content added via the block editor.
- Serve Next-gen Formats: Convert images to WebP format. There are plugins like ShortPixel or Imagify that can do this for you.
- Adaptive Images: Use a solution to serve different image sizes based on the visitor's device.
- Critical Images: Only load above-the-fold images initially. Lazy load the rest as the user scrolls.
Avoid Serving Legacy JavaScript to Modern Browsers:
- Use Babel: If you're developing custom themes or plugins, use a tool like Babel to transpile your JavaScript and use the nomodule attribute to serve modern JavaScript to modern browsers.
- Check Plugins and Themes: It's possible one of your plugins or your theme is including legacy JS. It may be worth reaching out to the developers for an update.
Find more tips by the link: https://onilab.com/blog/magento-2-performance-speed-optimization-guide
-
Hello,
If your website page speed is not increasing, then you must use the websitespeedy tool to help identify performance issues and optimize your website speed. Here are some steps you can take:
Run a speed test: Visit websitespeedy.com and enter your website's URL. The tool will analyze your website's speed and provide a report with recommendations for improvement.
Optimize images: Use an image compression tool like TinyPNG or Smush to compress your images and reduce their file size without compromising their quality. Additionally, ensure that the images are in the correct format (JPG, PNG, GIF) and are optimized for the web.
Preload HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Preloading HTML, CSS, and JavaScript can help reduce the time it takes for your web pages to load. By preloading these files, you can reduce the time it takes for your web pages to be delivered to your users.
Minimize render-blocking resources: Optimize your website's CSS and JavaScript files to reduce the time it takes to render the page.
Use LazyLoad: LazyLoad is a technique that helps reduce the amount of bandwidth needed to load a page by only loading content when it is needed. LazyLoad can help improve your Page Speed Score by reducing the amount of time it takes for content to be delivered to users.
By implementing these optimizations, you should be able to improve the speed and performance of your website.
-
@frazashfaq11 it also seems that you are suffering from slow server initial response time. I would suggest looking at that as a priority too, this can often counteract any work you are doing to optimise the speed of your site.
What hosting are you on? Is it shared hosting or a VPN?
-
Hi! I am SEO specialist at MjSeo. To solve your problem try to:
- Minimise HTTP requests.
Reduce and merge files.
Now that you know how many requests your site makes, you can start reducing that number. The best place to start is with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files. - use asynchronous loading for CSS and JavaScript files.
- defer the loading of the JavaScript file.
Delaying a file means preventing it from loading until other elements are loaded. If you defer large files such as JavaScript, you ensure that the rest of your content can load without delay. - Minimise the time to the first byte
In addition to the amount of time it takes for your page to fully load, you'll also want to look at the amount of time it takes to start loading. - Reduce server response time.
- One of the most important factors affecting the loading speed of your page is the time it takes for DNS to look up the page.
- DNS, or Domain Name System, is a server with a database of IP addresses and associated host names. When a user enters a URL into their browser, a DNS server translates that URL into an IP address that points to their location on the network.
- Thus, DNS lookup is the process of finding a particular DNS record. You can think of it as your computer looking up a number in the phone book.
- Translated with www.DeepL.com/Translator (free version)
You also can read here to find more useful information.
- Minimise HTTP requests.
-
@frazashfaq11 Hi! I think the Lighthouse output tells you that while you might have resized the images correctly in Photoshop, the width & height attributes aren't added to your image tags in HTML. So what is happening is that the browser can't reserve the actual space for the image upfront as it has to wait for the image to be loaded.
Got a burning SEO question?
Subscribe to Moz Pro to gain full access to Q&A, answer questions, and ask your own.
Browse Questions
Explore more categories
-
Moz Tools
Chat with the community about the Moz tools.
-
SEO Tactics
Discuss the SEO process with fellow marketers
-
Community
Discuss industry events, jobs, and news!
-
Digital Marketing
Chat about tactics outside of SEO
-
Research & Trends
Dive into research and trends in the search industry.
-
Support
Connect on product support and feature requests.
Related Questions
-
Customer Reviews on Product Page / Pagination / Crawl 3 review pages only
Hi experts, I present customer feedback, reviews basically, on my website for the products that are sold. And with this comes the ability to read reviews and obviously with pagination to display the available reviews. Now I want users to be able to flick through and read the reviews to help them satisfy whatever curiosity they have. My only thinking is that the page that contains the reviews, with each click of the pagination will present roughly the same content. The only thing that changes is the title tags which will contain the number in the H1 to display the page number. I'm thinking this could be duplication but i have yet to be notified by Google in my Search console... Should i block crawlers from crawling beyond page 3 of reviews? Thanks
Technical SEO | | Train4Academy.co.uk0 -
1000 Pages on old website. What to do with the 301 redirects for this domain?
Hi Moz Community, I have a 301 redirect question... I just acquired an old domain: Totally in my niche Domain is 14 years old Website exists of 1000 pages Great amount of backlinks Website is offline since about 2 weeks Will place a new website online asap with new url structure For the 50 best scoring pages I wrote a new, but fully comparable/related article. I will put a 301 redirect from those old to the new pages. My question: What to do with the 950 other url's? Should I put a 301 redirect to the homepage? Should I forward those pages to the 404 page? Should I divide the 950 url's with a 301 redirect to the 50 new ones? Another solution maybe? Any idea what would be the best solution so we can save as much Google juice as possible? Thanks in advance!
Technical SEO | | snorkel0 -
Car Dealership website - Duplicate Page Content Issues
Hi, I am currently working on a large car dealership website. I have just had a Moz crawl through and its flagging a lot of duplicate page content issues, these are mostly for used car pages. How can I get round this as the site stocks many of the same car, model, colour, age, millage etc. Only unique thing about them is the reg plate. How do I get past this duplicate issue if all the info is relatively the same? Anyone experienced this issue when working on a car dealership website? Thank you.
Technical SEO | | karl621 -
Blog Page Titles - Page 1, Page 2 etc.
Hi All, I have a couple of crawl errors coming up in MOZ that I am trying to fix. They are duplicate page title issues with my blog area. For example we have a URL of www.ourwebsite.com/blog/page/1 and as we have quite a few blog posts they get put onto another page, example www.ourwebsite.com/blog/page/2 both of these urls have the same heading, title, meta description etc. I was just wondering if this was an actual SEO problem or not and if there is a way to fix it. I am using Wordpress for reference but I can't see anywhere to access the settings of these pages. Thanks
Technical SEO | | O2C0 -
Is it good to redirect million of pages on a single page?
My site has 10 lakh approx. genuine urls. But due to some unidentified bugs site has created irrelevant urls 10 million approx. Since we don’t know the origin of these non-relevant links, we want to redirect or remove all these urls. Please suggest is it good to redirect such a high number urls to home page or to throw 404 for these pages. Or any other suggestions to solve this issue.
Technical SEO | | vivekrathore0 -
How to inform Google to remove 404 Pages of my website?
Hi, I want to remove more than 6,000 pages of my website because of bad keywords, I am going to drop all these pages and making them ‘404’ I want to know how can I inform google that these pages does not exists so please don’t send me traffic from those bad keywords? Also want to know can I use disavow tool of google website to exclude these 6,000 pages of my own website?
Technical SEO | | renukishor4 -
What is the best way to find missing alt tags on my site (site wide - not page by page)?
I am looking to find all the missing alt tags on my site at once. I have a FF extension that use to do it page by page, but my site is huge and that will take forever. Thanks!!
Technical SEO | | franchisesolutions1 -
Sitemap for dynamic website with over 10,000 pages
If I have a website with thousands of products, is it a good idea to create a sitemap for this website for the search engines where you show maybe 250 products on a page so it makes it easy for the search engine to find the part and also puts that part closer to the home page? Seems like google likes pages that are the closest to the home page (less clicks the better)
Technical SEO | | roundbrix0